Python Object-Oriented Programming
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) 란?
구성요소
- 객체 : 일종의 물건 - 물건은 일종의 **속성(attribute)**와 행동(Action)을 가짐.
- OOP는 이러한 객체 개념을 프로그램으로 표현하며, 각각 **변수(variable), 함수(method)**로 표현
구조
- class / instance
- class는 설계도, instance는 실제 구현체. 비유하자면 class는 붕어빵 틀, instance는 붕어빵. 한 붕어빵 틀(class)로 여러 종류의 붕어빵(instance)를 만들 수 있음.
인공지능 축구 프로그램으로 객체지향 이해하기
- 객체 - 팀, 선수, 심판
- method(def) - 공을 차다, 패스하다 (선수) / 휘슬 불다, 경고주다 (심판)
- variable - 이름, 포지션, 등 번호 (선수) / 팀 이름, 팀 연고지, 팀의 선수 (팀)
→ 각 객체에 연결되는 method와 variable이 있음

class SoccerPlayer(object): #class 선언
def __init__(self, name, position, back_number): # 객체 초기화 예약 method
self.name = name
self.position = position
self.back_number = back_number
def change_back_number(self, new_number): #method 구현
print("선수의 등번호를 변경합니다 : From %d to %d" % (self.back_number, new_number))
self.back_number = new_number
jinhyun = SoccerPlayer("Jinhyun", "MF", 10) #object 선언 // __init__함수 참고__init__함수의 변수 값 변경
def change_back_number(self,new_number):
print("등번호 From %d to %d" % (self.back_number, new_number))
self.back_number =new_number
jinhyun.change_back_number(5)
jinhyun.back_number(5) # 이렇게도 변경할 수 있음. but 권장 x
연습 - 노트북 만들기


class Note(object):
def __init__(self, content =None):
self.content =content
def write_content(self, content):
self.content = content
def remove_all(self):
self.content =""
def __add__(self,other): #합 반환
return self.content + other.content
def __str__(self): #출력
return self.content
class Notebook(object):
def __init__(self, title):
self.title = title
self.page_number = 1
self.notes ={}
def add_note(self, note, page =0):
if self.page_number <300:
if page ==0:
self.notes[self.page_number] =note
self.page_number +=1
else :
self.notes = {page : note}
self.page_number +=1
else:
print("페이지 꽉 참")
def remove_note(self, page_number) :
if page_number in self.note.keys():
return self.notes.pop(page_number)
else:
print("페이지 없음")
def get_number_pages(self):
return len(self.note.keys())
from 파일명 import Note
from 파일명 import Notebook
my_notebook =Notebook("수업1 강의노트")
new_note =Note("쿠쿠루")
new_note2 =Note("삥빵뽕")
my_notebook.add_note(new_note)
my_notebook.add_note(new_note2, 100) #특정 페이지에 노트 추가
# print(my_notebook.note[100]) - 삥빵뽕 - 만약 페이지 정보 없다면 KeyError
Inheritance(상속)



Polymorphism(다형성)

Visibility(가시성)
- 객체 정보를 볼 수 있는 레벨을 조정
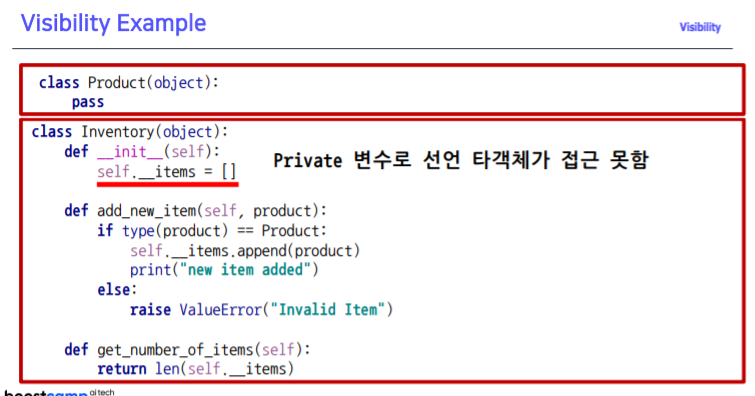
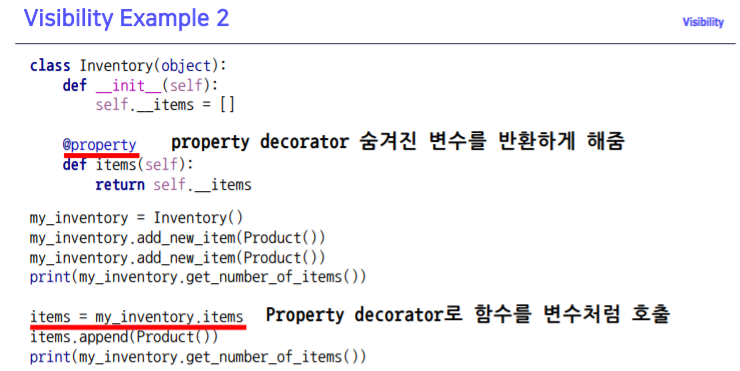
@ 의 사용
- first-class object
- inner function
- decorator


* 본 포스팅은 네이버 부스트캠프 AI Tech 3기 Pre-Course 강의를 정리한 내용입니다. https://www.boostcourse.org/onlyboostcampaitech3/joinLectures/329
'Study > Basics' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Basic Machine Learning : Supervised Learning (0) | 2022.01.17 |
|---|---|
| Module and Package (0) | 2021.12.29 |
| RNN (0) | 2021.12.29 |
| CNN (0) | 2021.12.29 |
| Optimization (0) | 2021.12.29 |